PATOGENITAS ISOLAT BAKTERI ASAM LAKTAT DARI USUS IKAN REPANG (Puntioplites waandersi) TERHADAP IKAN NILA (Oreochromis niloticus)
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.36706/jari.v11i1.55Keywords:
Lactid Acid Bacteria, Pathogenicity, A. hydrophila, HematologyAbstract
This study aims to determine the pathogenicity of lactic acid bacteria from repang fish on
clinical symptoms, anatomical pathology, hematology and survival rate of tilapia. This study
used a completely randomized design with 5 treatments and 3 replications, namely Phosphate
Bufferet Saline (PBS) 0.1 ml/fish as a negative control, A. hydrophila 106 CFU/ml as a
negative control, Enterococcus sp. 106 CFU/ml, Lactobacillus sp. 106 CFU/ml and
Lactococcus sp. 106 CFU/ml, fish given intramuscularly. Parameters observed included
clinical symptoms, anatomical pathology. Hematology and survival. Tilapia with an average
weight of 30 g/fish were reared for 7 days in an aquarium measuring 50×40×30 cm3 with a
volume of 40 L of water, at a density of 10 fish/aquarium. Fish are fed 3 times a day.
Administration of lactic acid bacteria Lactobacillus sp. showed the highest survival
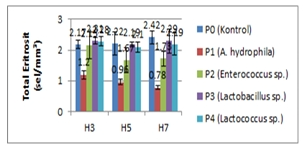
compared to the treatment with other isolates. Hematological parameters were in the normal
range in all treatments except for the treatment with A. hydrophila bacteria. Changes in
clinical symptoms of tilapia treated with injection with A. hydrophila showed clinical
symptoms of swimming patterns, decreased appetite and also moved more hyperactively. In
fish treated with Enterococcus sp., Lactococcus sp., and Lactobacillus sp. generally shows
normal condition. Anatomical changes in fish treated with A. hydrophila bacteria showed
changes in the form of excess mucus, redness on the back, pale body and easily detached
scales. The three lactic acid bacteria from the intestines of repang fish are safe for tilapia and
can be used in further probiotic tests.